Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a naturally occurring form of vitamin B3 that's popular in the realm of longevity sciences.
And while aging is a natural part of life, it doesn't mean we have to resign ourselves to a miserable experience. After all, who wants to spend their golden years feeling tired, achy, and generally blah?
Nicotinamide riboside supplements has been suggested to support a healthier aging process as a precursor molecule to NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) coenzyme required in cellular processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression.
What Is Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)?
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3 (niacin).
Among the other forms of B3, like nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, NR is a relatively newer form that's becoming widely recognized as a potential anti-aging supplement.
Unlike the other B3s, nicotinamide riboside is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which is a coenzyme needed for many key biological processes within the cell, from mitochondrial function, DNA repair and gene expression.

With age, NAD levels naturally decline.
Scientists believe that this decline in NAD is linked with impaired mitochondrial function and age-related diseases. The research on NR's ability to increase NAD levels is promising, but more robust human studies are needed in this space.
Nevertheless, people use nicotinamide riboside supplements to increase NAD levels in the body to slow down the hands of time and support their overall health.
Nicotinamide Riboside in Anti-Aging Research

Looking at longevity studies broadly is also helpful to better understand nicotinamide riboside.
Anti-aging research focuses on understanding the biological processes that underlie aging and developing interventions to slow and, in some cases, reverse the aging process.
As we age, our cells and tissues undergo changes, including the accumulation of DNA damage, changes in metabolism, and changes in gene expression.
All these changes lead to a decline in physical and cognitive function and can increase the risk of age-related diseases from high blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.
The field of anti-aging research looks at developing interventions to fight back against Father Time and allow people to live longer and healthier lives.
This may involve drug developments or supplements targeting specific aging pathways—like compounds that support NAD levels.
Of course, there are other ways to promote longevity, including lifestyle factors like exercise, diet, fasting, and reducing stress levels.
Ultimately, anti-aging science aims to help people live longer, healthier lives, free from the physical and cognitive decline that often accompanies aging.
NR to NAD Process
So we know that nicotinamide riboside (NR) is important because it can be transformed into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which is involved in many key cellular processes, but how does NR turn into NAD?
The transformation of NR into NAD occurs through a process called the NAD+ salvage pathway.
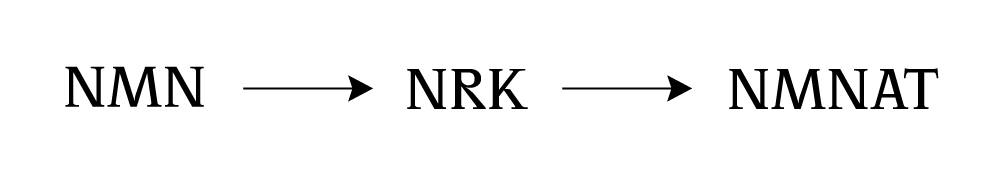
Don't be afraid of the long names of these enzymes coming up, the process is fairly straightforward to follow.
NR is first converted into another molecule called nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) by an enzyme called nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK), and that compound is what's converted into NAD by another enzyme called nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT).
You can think of this pathway as a factory assembly line.
NR is like the raw material that enters the factory, and NAD+ is the final product. And just as a factory requires a precise order of operations to work effectively, NAD+ requires a specific sequence of steps.
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is the oxidized form of NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). In other words, NAD+ is a molecule that has lost electrons and is in a high-energy state. Scientists believe that the specific levels of NAD+ are important for many longevity health benefits.
Nicotinamide Riboside Benefits
Nicotinamide riboside is the most studied compared to other longevity supplements that increase NAD levels, but it's worth noting that the research on NR is still relatively new and ongoing, most of which are preclinical trials (in vitro and animal models) with promising results.
NR supplements are believed to support various health benefits, such as improved mitochondrial function, increased longevity, and potential protection against age-related diseases.
1. NR Has Been Shown To Increase NAD+ Levels
One study looked at healthy humans and mice and found that taking an oral daily dose of 1000 mg of nicotinamide riboside (NR) twice a day (for a total of 2000 mg) can boost the amount of NAD+ in your bloodstream.
The research found that after just one dose, the NAD+ levels in the blood went up by 2.7 times without serious adverse effects [3].
Personal accounts of people taking NR supplements report generally having more energy and feeling more focused, but not in the same way as taking an energy drink or a cup of coffee. NR and NAD+ work at a cellular level to support its overall health benefits.
2. May Support Mitochondrial Function
The mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell — you may have remembered that line from your high school biology class as the mitochondria produce energy for all cellular activity. NR is believed to support mitochondrial function in a few ways before it is converted into NAD+.
The small size of the NR molecule can enter the cell easily and has been shown to increase levels of a molecule called mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), involved in regulating energy expenditure and heat production in the mitochondria, supporting its overall function to generate ATP—the cells' energy currency [4].
3. May Support Cardiovascular Health
Aging is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
NR has been shown to improve cardiovascular health by enhancing the function of cells that line blood vessels and by reducing inflammation in the body. In humans, a small study found that nicotinamide riboside supplements improved arterial stiffness, a measure of blood vessel health, in middle-aged and older adults with mild hypertension [5].
Additionally, it has been found to decrease the risk of developing heart disease in animal studies [6].
4. May Support People In Achieving A Healthier Body Weight
Another popular use of NR supplements is for weight control, and some evidence may support this.
A study conducted on healthy obese humans found that taking one gram of nicotinamide riboside daily for a period of six weeks altered body composition and increased skeletal muscle acetylcarnitine concentrations, which is important for metabolizing fats in the body [7].
It's been suggested that higher levels of skeletal muscle acetylcarnitine concentrations may indicate mitochondrial function, better energy, improved muscle function, and overall health.
Another contributing factor to managing health weight is insulin sensitivity.
In studies on mice, NR has been shown to improve their ability to process glucose, reduce weight gain, and protect against nerve damage and liver disease associated with diabetes by increasing NAD+ metabolism [8].
It's important to note that while some studies have shown promising results, more research is needed to understand the potential health benefits of NR supplementation fully. Additionally, speaking with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen is always important.

NR Supplement Benefits
Nicotinamide riboside supplements have been around for a while and have been extensively studied to compared to other NAD+ precursors. NR supplementation is generally safe for most healthy adults and is the best precursor to benefit our NAD levels.
While more human studies are needed to fully understand the effects of NR, early studies suggest that it may be a valuable tool for supporting overall wellness, particularly in aging, cardiovascular health, and metabolic health.
Some of the side effects of taking NR typically involve gastrointestinal discomfort (stomach discomfort, diarrhea, nausea), fatigue, and headaches. It's also possible for NR to interact with certain medications that affect blood glucose levels and blood pressure.
So what exactly is NR?
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a promising dietary supplement that may offer a range of potential health benefits.
As a form of vitamin B3, NR helps to increase levels of the important coenzyme NAD+ in cells, which plays a key role in energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, and many other cellular processes.
Common Questions About NR
1. What is nicotinamide riboside chloride?
Nicotinamide riboside chloride is a form of nicotinamide riboside (NR) that has been combined with chloride ions to form a stable salt. Selleckchem are among the only brands online selling this, you can check it out here.
This form of NR is commonly used in dietary supplements and is believed to have similar benefits to regular NR, such as supporting NAD+ levels and promoting cellular health. The addition of chloride ions is intended to improve the stability and bioavailability of the compound.
2. How does nicotinamide riboside (NR) work in the body?
NR is converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) in the body, which plays a key role in energy metabolism and cellular function. NR is also believed to support mitochondrial health and promote healthy aging.
3. What does Nicotinamide Riboside Do?
NR (nicotinamide riboside) is a form of vitamin B3 that may provide a range of potential health benefits. By increasing levels of the coenzyme NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) in cells, NR supplementation may support healthy energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, aging and longevity, neuroprotection, cardiovascular health, and metabolic health.
NAD+ is involved in a range of cellular processes in the body, and NR may help to support healthy function across many different systems. While the research on NR is still emerging, these potential benefits suggest that NR may be a promising supplement for supporting overall health and wellness.
4. Is Nicotinamide Riboside Safe?
Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is generally considered safe, although it may cause mild side effects such as upset stomach or diarrhea. As with any supplement, it's advised that you consult with a healthcare provider before taking NR, especially if you are pregnant or have a medical condition.
Taking nicotinamide riboside (NR) supplements on an empty stomach is generally safe. However, following the instructions on the supplement label or consult with a healthcare professional before taking any dietary supplement is always recommended.
5. Where can I find NR supplements?
NR supplements are available from various manufacturers and can be purchased online or at health food stores, but it's important to look at the purity of your supplement and third-party testing to ensure the product has been tested for safety.
Another thing to look for is to match the recommended daily dose (as per human studies) of around 300-500 mg to ensure the daily supplements are effective.
Resources:
-
Bieganowski, P., & Brenner, C. (2004). Discoveries of nicotinamide riboside as a nutrient and conserved NRK genes establish a Preiss-Handler independent route to NAD+ in fungi and humans. Cell, 117(4), 495-502.
-
Poljsak, B., Kovač, V., & Milisav, I. (2020). Healthy lifestyle recommendations: Do the beneficial effects originate from NAD+ amount at the cellular level?. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2020.
-
Trammell, S. A., Schmidt, M. S., Weidemann, B. J., Redpath, P., Jaksch, F., Dellinger, R. W., ... & Brenner, C. (2016). Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans. Nature communications, 7(1), 12948.
-
Mehmel, M., Jovanović, N., & Spitz, U. (2020). Nicotinamide riboside—the current state of research and therapeutic uses. Nutrients, 12(6), 1616.
-
Martens, C., Denman, B., Mazzo, M., Armstrong, M., Reisdorph, N., McQueen, M., ... & Seals, D. (2017). NAA1 nicotinamide riboside supplementation reduces aortic stiffness and blood pressure in middle-aged and older adults. Artery Research, 20(C), 49-49.
-
Winnik, S., Auwerx, J., Sinclair, D. A., & Matter, C. M. (2015). Protective effects of sirtuins in cardiovascular diseases: from bench to bedside. European heart journal, 36(48), 3404-3412.
-
Remie, C. M., Roumans, K. H., Moonen, M. P., Connell, N. J., Havekes, B., Mevenkamp, J., ... & Schrauwen, P. (2020). Nicotinamide riboside supplementation alters body composition and skeletal muscle acetylcarnitine concentrations in healthy obese humans. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 112(2), 413-426.
-
Trammell, S. A., Weidemann, B. J., Chadda, A., Yorek, M. S., Holmes, A., Coppey, L. J., ... & Brenner, C. (2016). Nicotinamide riboside opposes type 2 diabetes and neuropathy in mice. Scientific reports, 6(1), 26933.





